What Type of Battery is a Car Battery. They consist of lead plates and an electrolyte solution of sulfuric acid. Beyond starting the car, they power essential electrical components like lights, radios, and onboard computers.
Car batteries are crucial for vehicle operation. They supply the initial burst of energy needed to start the engine. Beyond starting the car, they power essential electrical components like lights, radios, and onboard computers. Lead-acid batteries are the most common type, known for their reliability and cost-effectiveness.
They consist of lead plates and an electrolyte solution of sulfuric acid. Proper maintenance can extend a car battery’s lifespan, ensuring optimal performance. Understanding the type and function of car batteries helps in making informed decisions for replacements and maintenance, enhancing vehicle reliability.

Credit: www.spinny.com
The Essence Of Car Batteries
Car batteries are the lifeblood of any vehicle. They provide the essential power needed to start the engine. Without a good battery, your car won’t run. Understanding car batteries is crucial for every vehicle owner.
Critical Role In Vehicle Operation
A car battery powers the starter motor and ignition system. It also supplies power to lights and other accessories. Without a car battery, these systems would fail.
Car batteries are usually lead-acid batteries. They are reliable and provide a steady power source. Modern cars need batteries to power advanced electronics too.
Here is a quick look at the critical functions of a car battery:
- Starting the engine
- Powering lights and accessories
- Stabilizing voltage
Evolution From Past To Present
Car batteries have evolved significantly over the years. Early car batteries were simple and less efficient. They often required frequent maintenance.
Modern car batteries are more advanced. They are maintenance-free and last longer. Innovations in technology have improved battery life and efficiency.
Here is a table showing the evolution of car batteries:
| Time Period | Battery Type | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Early 1900s | Lead-Acid | Basic, High Maintenance |
| Mid 1900s | Lead-Acid | Improved Efficiency |
| 2000s Onwards | Advanced Lead-Acid | Maintenance-Free, Long-Lasting |
Future batteries may include more lithium-ion options. These are lighter and more efficient. The evolution of car batteries continues to enhance vehicle performance.
Diving Into Battery Chemistry
Understanding car battery chemistry helps you choose the right one for your vehicle. Different types of batteries use different chemical reactions. These reactions power your car’s electrical systems. Let’s explore the most common types.
Lead-acid: The Traditional Choice
Lead-acid batteries are the most common type of car battery. They have been around for over a century. These batteries are reliable and cost-effective. Lead-acid batteries use lead plates and sulfuric acid. The chemical reaction between them creates electricity.
There are two main types of lead-acid batteries:
- Flooded Lead-Acid Batteries: These are the most common. They need regular maintenance. You must check and refill the water levels.
- Sealed Lead-Acid Batteries: These are also known as maintenance-free batteries. They do not require water refills. They are usually more expensive than flooded batteries.
Agm And Gel: Enhanced Lead-acid Variants
AGM and Gel batteries are improved versions of lead-acid batteries. They offer better performance and durability.
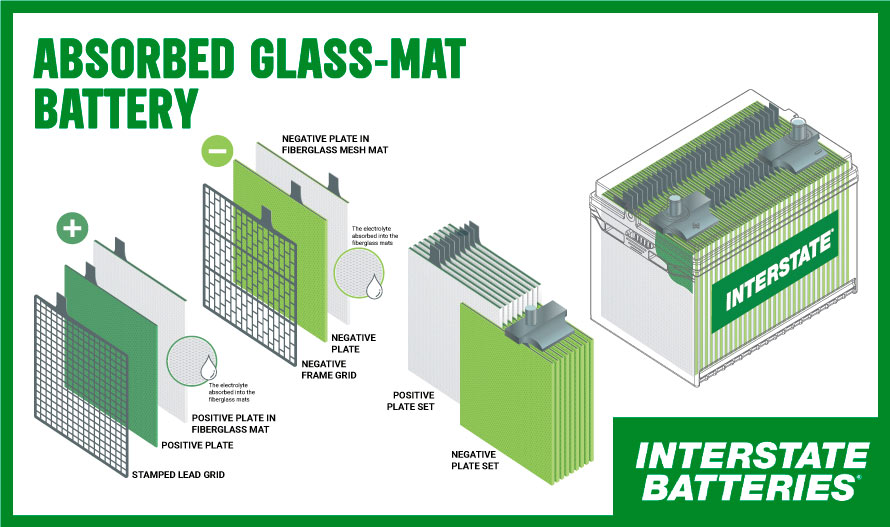
AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) Batteries use a special glass mat. This mat absorbs the sulfuric acid. They are more resistant to vibration and shock. They also recharge faster and last longer.
Gel Batteries use a gel-like substance instead of liquid acid. This gel prevents leaks and spills. Gel batteries work well in extreme temperatures. They are also more resistant to deep discharges.
Here is a comparison table:
| Battery Type | Maintenance | Durability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flooded Lead-Acid | High | Moderate | Low |
| Sealed Lead-Acid | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| AGM | Low | High | High |
| Gel | Low | High | High |
Choosing the right battery depends on your needs. Consider the maintenance, durability, and cost. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these can help you make an informed decision.
Lithium-ion: The Modern Contender
Lithium-Ion batteries are becoming popular in the automotive world. They offer many benefits over traditional car batteries. These batteries are found in electric vehicles and some hybrid cars. They are lightweight, powerful, and efficient.
Advantages Over Traditional Batteries
- Lightweight: Lithium-Ion batteries are lighter than lead-acid batteries. This makes them ideal for cars, as it helps improve fuel efficiency.
- Higher Energy Density: They store more energy in a smaller space. This means cars can travel longer distances on a single charge.
- Longer Lifespan: These batteries last longer than traditional ones. They can handle more charge and discharge cycles.
- Faster Charging: Lithium-Ion batteries charge faster. This reduces the downtime for electric vehicles.
- Low Maintenance: They require little to no maintenance. This saves time and money for car owners.
Considerations For Automotive Use
While Lithium-Ion batteries have many benefits, there are some things to consider. These batteries can be more expensive than traditional ones. The initial cost is higher, but the long-term savings can be worth it.
Temperature sensitivity is another factor. Lithium-Ion batteries can be affected by extreme temperatures. They may not perform well in very hot or cold weather. Proper thermal management systems can help mitigate this issue.
Safety is also important. Lithium-Ion batteries can pose a fire risk if damaged or improperly handled. Manufacturers are working to improve safety features and reduce these risks.
Despite these considerations, Lithium-Ion batteries are a strong contender in the automotive industry. They offer many advantages that make them a preferred choice for modern vehicles.
Analyzing Battery Specifications
Understanding the specifications of a car battery is crucial for selecting the right one. These specifications tell you how the battery performs and fits your car’s needs. Let’s dive into two key specifications: capacity and voltage, and cold cranking amps.
Understanding Capacity And Voltage
The capacity of a car battery is measured in ampere-hours (Ah). This tells you how much energy the battery can store. For example, a 50Ah battery can deliver 5 amps for 10 hours.
Voltage is another important specification. Most car batteries are 12 volts. This means the battery can provide a steady 12 volts of power to your vehicle’s electrical system. Proper voltage ensures your car’s electronics work efficiently.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Capacity (Ah) | Measures energy storage. Higher Ah means longer power supply. |
| Voltage (V) | Standard is 12V. Ensures efficient functioning of car electronics. |
The Importance Of Cold Cranking Amps
Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) is crucial for starting your car, especially in cold weather. CCA measures the battery’s ability to start an engine in cold temperatures. A higher CCA rating means better performance in cold conditions.
For instance, a battery with 600 CCA can start an engine even at low temperatures. This is essential for reliable starting during winter.
- Higher CCA: Better cold-weather performance.
- Low CCA: May struggle in cold conditions.
Always check the CCA rating before buying a car battery. It ensures your car starts easily, no matter the weather.
Maintenance And Longevity Tips
Car batteries are essential for vehicle operation. Proper maintenance and care can extend their life. Here are some tips to help you keep your car battery in top shape.
Regular Check-ups For Optimal Performance
Regular check-ups are crucial for optimal battery performance. Inspect your battery every month. Look for any signs of corrosion or damage.
- Clean the terminals: Use a mixture of baking soda and water. This will prevent corrosion.
- Check the fluid levels: If the battery is not sealed, ensure the fluid is at the right level. Use distilled water to top up if needed.
- Test the voltage: Use a multimeter to check the voltage. A fully charged battery should read 12.6 volts or higher.
Extending Your Battery’s Life
Extending your battery’s life requires some simple practices. These habits will help you avoid premature battery failure.
- Avoid short trips: Short trips don’t give the battery enough time to recharge. Combine errands to allow the battery to recharge fully.
- Turn off lights and accessories: Ensure all lights and electronic accessories are off when the car is not running. This prevents unnecessary battery drain.
- Keep the battery secure: Ensure the battery is tightly fastened. A loose battery can cause internal damage and short circuits.
- Store properly: If the car will be parked for a long time, disconnect the battery or use a trickle charger. This keeps the battery charged and ready to use.
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Clean terminals | Monthly |
| Check fluid levels | Every 3 months |
| Test voltage | Every 6 months |
By following these maintenance and longevity tips, you can ensure your car battery stays in good condition. This will help you avoid unexpected breakdowns and save money in the long run.
Recycling And Environmental Impact
Car batteries are essential for modern vehicles, but they have a significant environmental impact. Understanding the recycling process and reducing the ecological footprint is crucial.
The Process Of Battery Recycling
The process of recycling car batteries involves several steps:
- Collection: Old batteries are collected from various sources.
- Sorting: Batteries are sorted by type and condition.
- Breaking: Batteries are broken down into smaller pieces.
- Separation: Components are separated into lead, plastic, and acid.
- Processing: Each material is processed for reuse.
Recycling batteries reduces waste and conserves natural resources. The lead from old batteries can be reused in new batteries. Plastic and acid are also recycled, reducing environmental harm.
Reducing The Ecological Footprint
Reducing the ecological footprint of car batteries involves several strategies:
- Use Rechargeable Batteries: They last longer and reduce waste.
- Proper Disposal: Dispose of batteries at designated recycling centers.
- Support Green Manufacturing: Choose batteries made with eco-friendly materials.
- Advocate for Regulations: Support laws that promote battery recycling.
Adopting these practices helps protect the environment and conserve resources. Consumers can make a difference by choosing eco-friendly options and supporting recycling initiatives.
What Type of Battery is a Car Battery STD, AGM, or Gel?
When choosing a car battery, it’s essential to know the differences between Standard Flooded (STD), Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM), and Gel batteries. Each type has its unique characteristics and benefits.
1. Understand the Basics of Car Batteries
Car batteries provide the necessary power to start your vehicle and run its electrical systems. They convert chemical energy into electrical energy to start the engine and power accessories.
2. Recognize Standard Flooded (STD) Batteries
Standard Flooded batteries, also known as wet cell batteries, are the most common type. They contain liquid electrolyte and require regular maintenance. These batteries are cost-effective and suitable for many standard vehicles.
3. Identify Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) Batteries
AGM batteries are advanced type of lead-acid battery. They use fiberglass mats to hold the electrolyte, making them spill-proof and maintenance-free. AGM batteries provide higher power output, making them ideal for modern vehicles with high electrical demands and start-stop technology.
4. Learn About Gel Batteries
Gel batteries use a gel-like electrolyte. They are designed for deep-cycle applications and are often used in recreational vehicles and marine applications. Gel batteries are also maintenance-free and spill-proof but are more expensive and less common in standard vehicles.
5. Compare Performance and Lifespan
- STD Batteries: Typically last 3-5 years and require regular maintenance.
- AGM Batteries: Offer a lifespan of 4-7 years and are maintenance-free.
- Gel Batteries: Can last up to 10 years, ideal for deep-cycle applications but less common in everyday vehicles.
6. Evaluate Your Vehicle’s Needs
Consider your vehicle’s electrical demands and usage. Modern cars with advanced electronics and start-stop systems benefit more from AGM batteries, while standard vehicles can often do well with STD batteries.
7. Consider Maintenance Requirements
- STD Batteries: Require regular maintenance, including checking and topping off electrolyte levels.
- AGM and Gel Batteries: Are maintenance-free, saving you time and effort.
8. Assess Environmental Conditions
If you live in an area with extreme temperatures, AGM batteries perform better in cold weather and have faster recharge times. Gel batteries also handle extreme conditions well but are more suited for specific applications.
9. Factor in Cost
- STD Batteries: Are the most cost-effective option.
- AGM Batteries: Cost more but provide better performance and longer lifespan.
- Gel Batteries: Are the most expensive and specialized for deep-cycle uses.
10. Make an Informed Decision
Based on your vehicle’s requirements, budget, and maintenance preferences, choose the battery type that best suits your needs. Always consult your vehicle’s manual or a professional mechanic to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
The Future Of Car Batteries
The landscape of car batteries is evolving rapidly. With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), there’s a growing need for efficient, durable, and environmentally friendly batteries. Let’s dive into the future of car batteries and see what innovations are on the horizon.
Innovations On The Horizon
One major development is the introduction of solid-state batteries. These batteries use solid electrolytes instead of liquid ones. This makes them safer and more energy-dense. Solid-state batteries could potentially double the range of electric vehicles.
Another innovation is the use of lithium-sulfur batteries. These have a higher energy density compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. They are also cheaper to produce. This makes them an attractive option for future electric vehicles.
Researchers are also exploring graphene-based batteries. Graphene is a form of carbon that is incredibly strong and conductive. These batteries could charge faster and last longer than current options.
Impact Of Electric Vehicles On Battery Technology
The rise of electric vehicles is driving rapid advancements in battery technology. Car manufacturers are investing heavily in research and development. This has led to the creation of batteries that are more efficient and environmentally friendly.
The demand for electric vehicles is also pushing the development of recycling technologies. Efficient recycling methods are crucial for managing the environmental impact of used batteries. This ensures a sustainable future for electric vehicles.
The shift towards electric vehicles is also fostering the growth of battery-as-a-service models. In this model, consumers can lease batteries rather than buy them. This reduces the upfront cost of electric vehicles and makes them more accessible to a wider audience.
| Innovation | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Solid-State Batteries | Safer, more energy-dense |
| Lithium-Sulfur Batteries | Higher energy density, cheaper production |
| Graphene-Based Batteries | Faster charging, longer lifespan |
In summary, the future of car batteries looks promising. With innovations like solid-state, lithium-sulfur, and graphene-based batteries, the automotive industry is on the brink of a revolution.

Credit: knowhow.napaonline.com

Credit: gomechanic.in
Frequently Asked Questions
Is A Car Battery Agm Or Std?
To determine if a car battery is AGM or STD, check the label or consult the vehicle manual. AGM stands for Absorbent Glass Mat, while STD refers to standard flooded batteries. AGM batteries are sealed, maintenance-free, and offer better performance.
What Type Of Battery Is Used In A Car?
Cars typically use lead-acid batteries. These are rechargeable and provide the necessary power to start the engine. Lead-acid batteries are cost-effective and reliable, making them the most common choice for automotive use.
Is My Car Battery Lithium Or Agm?
Check your car battery label. Lithium batteries are marked “Li-ion” or “Lithium. ” AGM batteries are labeled “AGM” or “Absorbent Glass Mat. “
What Type Of Battery Is A Car Battery Wet Or Dry?
Car batteries are typically wet cell batteries. They contain liquid electrolytes. These are also known as lead-acid batteries.
Conclusion
Understanding the type of battery your car uses is crucial. It ensures optimal performance and longevity. Always check your vehicle’s manual for battery specifications. Regular maintenance and timely replacements can save you from unexpected breakdowns. Stay informed and keep your car running smoothly.
Happy driving!